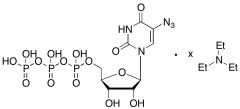
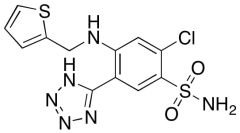
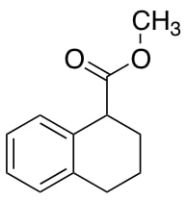
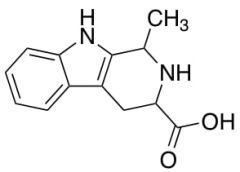
Differences Between Working Standards and Reference Standards

Working standards are examples of a substance or drug that are used as a point of reference during manufacturing. These standards are created by manufacturers and calibrated against reference standards. The goal of working standards is to make sure that the manufactured product adheres to necessary specifications and maintains uniformity. Laboratories frequently rely on working standards to assess the quality of products during the production process.
The Role of Working Standards
Working standards are essential in the pharmaceutical industry because they ensure that the final product meets critical safety and quality guidelines. These standards help to monitor the consistency and quality of the product throughout its manufacturing journey. By employing working standards, manufacturers can detect any deviations or irregularities and take the necessary corrective steps.
Additionally, working standards are crucial during the development phase of a product, helping to guarantee its consistency and stability. They are particularly important when new products are being developed, as they offer a benchmark for assessing product quality and uniformity.
Understanding Reference Standards
Reference standards, like working standards, are critical in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure that products meet the appropriate safety and quality benchmarks. These standards are used to validate the accuracy of working standards, making sure that regulatory requirements are fulfilled.
Reference standards are particularly important in the testing and analysis of healthcare products. They are commonly used to compare the properties of manufactured products with those of the reference standards. This comparison allows for precise measurement of a product’s identity, purity, quality, consistency, and strength.
The Connection Between Working Standards and Reference Standards
Working standards and reference standards are closely linked. Working standards are calibrated against reference standards to ensure their accuracy and reliability. Reference standards verify that working standards meet the required specifications and maintain consistency. They are also used to evaluate the accuracy of the final product. By comparing the product to reference standards, manufacturers can ensure that it meets regulatory standards.
Key Differences Between Working Standards and Reference Standards
There are several key differences between working standards and reference standards, with their primary purpose being the most significant. Working standards are used mainly to monitor the consistency and quality of a product during production, while reference standards are used to ensure that the final product complies with regulatory requirements.
Another key difference is their origin. Working standards are created by manufacturers and are usually calibrated against reference standards. Reference standards, on the other hand, are obtained from recognized sources, such as pharmacopeia.
Their applications also differ. Working standards are primarily used to assess product consistency and quality, whereas reference standards are mainly employed during testing to ensure products meet the necessary specifications.
Conclusion
In summary, both working standards and reference standards are vital to the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that products meet the required specifications and regulatory standards. Although they serve different purposes, they work in tandem to ensure quality. Given the importance of accuracy and precision in pharmaceuticals, it’s crucial to source high-quality materials from trusted certified reference materials suppliers.
 info@theclinivex.com
info@theclinivex.com  +1 (877)-861-1996
+1 (877)-861-1996